设计模式的理会和实现(C++)之十九-Memento模式
副标题#e#
浸染:
在不粉碎封装性的前提下,捕捉一个工具的内部状态,并在该工具之外生存这个状态.这样今后就可将该工具规复到原先生存的状态.
UML布局图:
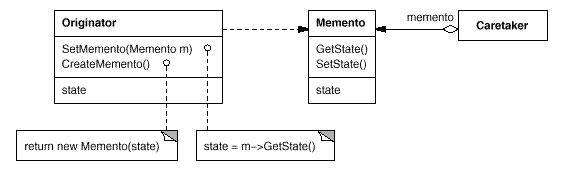
理会:
Memento模式中封装的是需要生存的状态,当需要规复的时候才取出来举办规复.道理很简朴,实现的时候需要留意一个处所:窄接口和宽接口.所谓的宽接口就是一般意义上的接口,把对外的接口作为public成员;而窄接口反之,把接口作为private成员,而把需要会见这些接口函数的类作为这个类的友元类,也就是说接口只袒露给了对这些接口感乐趣的类,而不是袒露在外部.下面的实现就是窄实现的要领来实现的.
实现:
1)Memento.h
/**//********************************************************************
created: 2006/08/09
filename: Memento.h
author: 李创
http://www.cppblog.com/converse/
purpose: Memento模式的演示代码
*********************************************************************/
#ifndef MEMENTO_H
#define MEMENTO_H
#include <string>
typedef std::string State;
class Memento;
class Originator
{
public:
Originator(const State& rState);
Originator();
~Originator();
Memento* CreateMemento();
void SetMemento(Memento* pMemento);
State GetState();
void SetState(const State& rState);
void RestoreState(Memento* pMemento);
void PrintState();
private:
State m_State;
};
// 把Memento的接口函数都配置为私有的,而Originator是它的友元,
// 这样担保了只有Originator可以对其会见
class Memento
{
private:
friend class Originator;
Memento(const State& rState);
void SetState(const State& rState);
State GetState();
State m_State;
};
#endif
#p#副标题#e#
2)Memento.cpp
/**//********************************************************************
created: 2006/08/09
filename: Memento.cpp
author: 李创
http://www.cppblog.com/converse/
purpose: Memento模式的演示代码
*********************************************************************/
#include "Memento.h"
#include <iostream>
Originator::Originator()
{
}
Originator::Originator(const State& rState)
: m_State(rState)
{
}
Originator::~Originator()
{
}
State Originator::GetState()
{
return m_State;
}
void Originator::SetState(const State& rState)
{
m_State = rState;
}
Memento* Originator::CreateMemento()
{
return new Memento(m_State);
}
void Originator::RestoreState(Memento* pMemento)
{
if (NULL != pMemento)
{
m_State = pMemento->GetState();
}
}
void Originator::PrintState()
{
std::cout << "State = " << m_State << std::endl;
}
Memento::Memento(const State& rState)
: m_State(rState)
{
}
State Memento::GetState()
{
return m_State;
}
void Memento::SetState(const State& rState)
{
m_State = rState;
}
3)Main.cpp
/**//********************************************************************
created: 2006/08/09
filename: Main.cpp
author: 李创
http://www.cppblog.com/converse/
purpose: Memento模式的测试代码
*********************************************************************/
#include "Memento.h"
int main()
{
// 建设一个原发器
Originator* pOriginator = new Originator("old state");
pOriginator->PrintState();
// 建设一个备忘录存放这个原发器的状态
Memento *pMemento = pOriginator->CreateMemento();
// 变动原发器的状态
pOriginator->SetState("new state");
pOriginator->PrintState();
// 通过备忘录把原发器的状态还原到之前的状态
pOriginator->RestoreState(pMemento);
pOriginator->PrintState();
delete pOriginator;
delete pMemento;
return 0;
}
