GPGPU OpenCL实现准确字符串查找
副标题#e#
字符串查找是信息安详、信息过滤规模的重要操纵,尤其是对大文本的及时处理惩罚。这篇作为实例,利用GPU OpenCL举办准确模式串查找。
1.加将近领
(1)将少量常量数据,如模式串长度、文本长度等,生存在线程的private memory中。
(2)将模式串生存在GPU的local memory中,加快线程对模式串的会见。
(3)将待查找的文本生存在global memory中,利用尽大概多线程会见global memory,减小线程平均访存时间。
(4)每个work-group中的线程操纵文本中一段,多个work-group并行处理惩罚大文本。
2.同步
(1)work-group内,利用CLK_LOCAL_MEM_FENCE、CLK_GLOBAL_MEM_FENCE
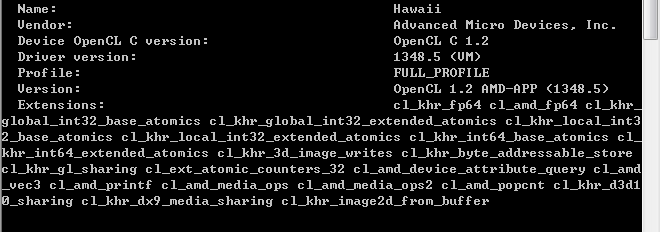
(2)全局利用对__global int 的原子操纵,来担保每个线程将功效写到全局内存的正确位置。设备支持的操纵可以通过查询设备的扩展得到,如下图,可知核函数支持原子操纵、printf操纵:
3.代码实例,大文本准确模式串搜索
3.1 核函数(string_search_kernel.cl):
int compare(__global const uchar* text, __local const uchar* pattern, uint length){
for(uint l=0; l<length; ++l){
if (text[l] != pattern[l])
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
__kernel void
StringSearch (
__global uchar* text, //Input Text
const uint textLength, //Length of the text
__global const uchar* pattern, //Pattern string
const uint patternLength, //Pattern length
const uint maxSearchLength, //Maximum search positions for each work-group
__global int* resultCount, //Result counts (global)
__global int* resultBuffer, //Save the match result
__local uchar* localPattern) //local buffer for the search pattern
{
int localIdx = get_local_id(0);
int localSize = get_local_size(0);
int groupIdx = get_group_id(0);
uint lastSearchIdx = textLength - patternLength + 1;
uint beginSearchIdx = groupIdx * maxSearchLength;
uint endSearchIdx = beginSearchIdx + maxSearchLength;
if(beginSearchIdx > lastSearchIdx)
return;
if(endSearchIdx > lastSearchIdx)
endSearchIdx = lastSearchIdx;
for(int idx = localIdx; idx < patternLength; idx+=localSize)
localPattern[idx] = pattern[idx];
barrier(CLK_LOCAL_MEM_FENCE);
for(uint stringPos=beginSearchIdx+localIdx; stringPos<endSearchIdx; stringPos+=localSize){
if (compare(text+stringPos, localPattern, patternLength) == 1){
int count = atomic_inc(resultCount);
resultBuffer[count] = stringPos;
//printf("%d ",stringPos);
}
barrier(CLK_LOCAL_MEM_FENCE);
}
}
#p#副标题#e#
3.2.tool.h 、tool.cpp
见:http://www.cnblogs.com/xudong-bupt/p/3582780.html
3.3 StringSearch.cpp
#include <CL/cl.h>
#include "tool.h"
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
cl_int status;
/**Step 1: Getting platforms and choose an available one(first).*/
cl_platform_id platform;
getPlatform(platform);
/**Step 2:Query the platform and choose the first GPU device if has one.*/
cl_device_id *devices=getCl_device_id(platform);
/**Step 3: Create context.*/
cl_context context = clCreateContext(NULL,1, devices,NULL,NULL,NULL);
/**Step 4: Creating command queue associate with the context.*/
cl_command_queue commandQueue = clCreateCommandQueue(context, devices[0], 0, NULL);
/**Step 5: Create program object */
const char *filename = "string_search_kernel.cl";
string sourceStr;
status = convertToString(filename, sourceStr);
const char *source = sourceStr.c_str();
size_t sourceSize[] = {strlen(source)};
cl_program program = clCreateProgramWithSource(context, 1, &source, sourceSize, NULL);
/**Step 6: Build program. */
status=clBuildProgram(program, 1,devices,NULL,NULL,NULL);
/**Step 7: Initial input,output for the host and create memory objects for the kernel*/
string textStr; //StringSearch_Input.txt
convertToString("StringSearch_Input.txt", textStr);
const char * text = textStr.c_str();
int textlen=strlen(text);
char * pattern="info";
int patternlen=strlen(pattern);
int maxSearchLength=256*64;
int * resultCount=new int[1];
*resultCount=0;
int * result=new int[textlen];
memset(result,0,sizeof(int)*textlen);
cl_mem textBuffer = clCreateBuffer(context, CL_MEM_READ_ONLY|CL_MEM_COPY_HOST_PTR, sizeof(char)*textlen,(void *)text, NULL); //global memory
cl_mem patternBuffer = clCreateBuffer(context, CL_MEM_WRITE_ONLY|CL_MEM_COPY_HOST_PTR ,sizeof(char)*patternlen, (void *)pattern, NULL);
cl_mem resultCountBuffer = clCreateBuffer(context, CL_MEM_WRITE_ONLY|CL_MEM_COPY_HOST_PTR ,sizeof(int), (void *)resultCount, NULL);
cl_mem resultBuffer = clCreateBuffer(context, CL_MEM_WRITE_ONLY|CL_MEM_COPY_HOST_PTR ,sizeof(int)*textlen, (void *)result, NULL);
/**Step 8: Create kernel object */
cl_kernel kernel = clCreateKernel(program,"StringSearch", NULL);
/**Step 9: Sets Kernel arguments.*/
status = clSetKernelArg(kernel, 0, sizeof(cl_mem), (void *)&textBuffer); //global
status = clSetKernelArg(kernel, 1, sizeof(int), &textlen); //private
status = clSetKernelArg(kernel, 2, sizeof(cl_mem), (void *)&patternBuffer); //global
status = clSetKernelArg(kernel, 3, sizeof(int), &patternlen); //private
status = clSetKernelArg(kernel, 4, sizeof(int), &maxSearchLength); //private
status = clSetKernelArg(kernel, 5, sizeof(cl_mem), (void *)&resultCountBuffer); //global
status = clSetKernelArg(kernel, 6, sizeof(cl_mem), (void *)&resultBuffer); //global
status = clSetKernelArg(kernel, 7, sizeof(char)*patternlen, NULL); //local
/**Step 10: Running the kernel.*/
cl_event enentPoint;
int globalWorkItem=textlen/64;
if(textlen%64 != 0)
globalWorkItem++;
size_t groupNUm[1]={globalWorkItem};
size_t localNUm[1]={256};
status = clEnqueueNDRangeKernel(commandQueue, kernel, 1, NULL, groupNUm, localNUm, 0, NULL, &enentPoint);
clWaitForEvents(1,&enentPoint); ///wait
clReleaseEvent(enentPoint);
int count=0;
status = clEnqueueReadBuffer(commandQueue, resultCountBuffer, CL_TRUE, 0, sizeof(int), &count, 0, NULL, NULL);
cout<<"\nNumber of matches:"<<count<<endl;
/**Step 12: Clean the resources.*/
status = clReleaseKernel(kernel);//*Release kernel.
status = clReleaseProgram(program); //Release the program object.
status = clReleaseMemObject(resultBuffer);//Release mem object.
status = clReleaseMemObject(textBuffer);//Release mem object.
status = clReleaseMemObject(resultCountBuffer);//Release mem object.
status = clReleaseMemObject(patternBuffer);//Release mem object.
status = clReleaseCommandQueue(commandQueue);//Release Command queue.
status = clReleaseContext(context);//Release context.
free(devices);
free(result);
free(resultCount);
getchar();
return 0;
}
作者:cnblogs 旭东的博客
